In the era of web automation and testing, locating elements effectively is a crucial stage for building powerful testing scripts. XML Path Language, or XPath stands out as the robust and versatile technique for navigating the Document Object Model (DOM) and detecting web components.
Whether you are dealing with conditional selections, deeply nested structures, or dynamic IDs, mastering XPath guarantees precise element location and controls flakiness in test implementation. Tools such as XPath tester ease this procedure by enabling QA Engineers to validate their XPath expressions in real-time, guaranteeing accurate element selection before incorporating them into scripts.
What is XPath, and why is it significant in Automation Testing?
It is a query language used to navigate through the structure of an XML doc, enabling QA Engineers in automation to specifically locate and interact with particular elements on a page (which is treated as an XML doc) based on their hierarchical attributes and relationships. This makes XPath an essential tool for detecting dynamically changing or complicated components in web tests, particularly when other locators such as class or ID names aren’t readily reliable or accessible. Eventually, XPath provides a robust method to pinpoint components within a page’s HTML structure for automation purposes.
Major Points about XPath in Automated Tests:
- Element Identification: XPath lets you locate components on a page using a path-like syntax, denoting the sequence of child-parent relationships to reach the preferred element.
- Flexibility: Unlike simpler locators, XPath can determine elements based on multiple criteria such as attribute values, text content, and relative positions within the Document Object Model (DOM), making it adaptable to complicated web structures.
- Dynamic Components: When dealing with dynamic web elements that change recurrently, XPath can be chiefly beneficial to locate them based on their relative position or different attributes that remain constant.
- Selenium Incorporation: In automated test frameworks such as Selenium, XPath is extensively used as a locator strategy to communicate with web components on a webpage.
Sample of XPath use: To find a search input field with the “q” on a webpage “name” attribute, you might utilize an XPath such as:
//input[@name=”q”]
What is an XPath Tester, and How Does It Aid in Automation?
An XPath tester is a feature or tool, often accessible in browser developer tools or standalone apps, that enables you to generate, test, and validate XPath expressions against a page’s DOM. It is a valuable resource in test automation, allowing QA Engineers to ensure that their XPath expressions correctly detect the desired web components before incorporating them into test scripts.
How an XPath Tester Assists in Automation?
- Accurate Element Identification
XPath testers enable you to test XPath expressions in real time, assisting you in checking that your XPath correctly locates the intended components. This reduces the chances of bugs in your automated scripts caused by incorrect XPath expressions.
- Troubleshooting & Debugging
When a test script fails to locate an element during implementation, an XPath tester can assist in debugging the problem by scrutinizing whether the XPath expression is valid for the current state of the Document Object Model (DOM).
Discover More: Susan Waren: From Political Aide to Joe Scarborough’s Ex-Wife
- Time Effectiveness
By allowing rapid validation, XPath testers save time during the development & debugging stages, enabling QA Engineers to refine XPath expressions without rerunning complete scripts repeatedly.
- Dynamic XPath Management
For pages with dynamic IDs or complicated nested structures, XPath testers assist in validating advanced expressions using functions such as text(), contains(), or axis navigation (following-sibling::, ancestor::, etc.)
- Cross-Browser Compatibility
Several browser developer tools like Firefox Inspector and Chrome DevTools, include built-in XPath testers. This guarantees that the XPath expressions you validate will function constantly across several browsers.
- Learning & Experimentation
XPath testers are exceptional at discovering and learning how XPath functions. By experimenting with diverse expressions, QA Engineers can master advanced techniques such as managing dynamic IDs, nested structures, and attribute-centric selection.
Example: How to Utilize an XPath Tester in Chrome Developer Tools
- Open the page you wish to test.
- Right-click the element you wish to locate & select Inspect.
- In the Elements tab, press Cmd + F (Mac) or Ctrl + F (Windows) to activate the search box.
- Input your XPath expression into the search box. The Document Object Model (DOM) will highlight matching components, and the number of matches will be displayed.
Major Strategies for Complicated XPath Scenarios
- Relative XPath for Flexibility
Unlike absolute XPath, which depends on a fixed hierarchy, relative XPath locates components based on their relationship with other recognized elements. This method is more resilient and dynamic to alterations in the Document Object Model (DOM) structure.
Sample:
//div[@class=”container”]/span[@class=”title”]
- Attribute-Centric Selection
- Partial Matching with Wildcards:
Use * to match portions of an attribute value when exact matches are impossible.
Sample:
//div[@class=”product-item*”]
- Contains Operator:
Use contains() to find components with partially matching attribute values.
Sample:
//a[contains(@href, “login”)]
- Axis Navigation for Traversing Hierarchies
- Child Axis: Find direct child components.
Sample:
//div[@id=”parent”]/child::button
- Descendant Axis: Locate components nested within a parent, despite depth.
Sample:
//form/descendant::input
- Following-Sibling Axis: Choose elements following a particular sibling.
Sample:
//div[@class=”product-details”]/following-sibling::div
- Text Node Matching
- Exact Text Match: Locate elements with precise text content.
Sample:
//button[text()=”Submit”]
- Contains Text Match: Select elements where the text partially matches a string.
Sample:
//button[contains(text(), “Add”)]
Example Circumstances for Advanced XPath
- Dynamic ID Handling
- Find elements based on a parent with a steady ID:
//div[@id=”product-container”]/child::a
- Find elements through a class that remains constant despite dynamic modifications:
//div[contains(@class, “dynamic-class”)]/button
- Extremely Nested Structures
- Access a particular component within multiple nested divs:
//div[@class=”main-container”]/div[@class=”section”]/div[@class=”item”]/a
- Find elements relative to a recognized element:
//div[@id=”header”]/following-sibling::div
Significant Considerations for XPath Mastery
- Leverage Browser Developer Tools
Examine the Document Object Model (DOM) structure via browser developer tools to generate and validate XPath expressions. Use traits such as the built-in “XPath Tester” to check your expressions’ accuracy.
- Comprehensive Tests
Continuously test your XPath expressions with multiple scenarios to guarantee consistent functionality across robust web pages.
- Performance Optimization
When possible, ease intricate XPath expressions, particularly when working with large Document Object Model (DOMs), to enhance performance and control implementation time.
Why Mastering XPath is Crucial in Test Automation?
XPath plays a pivotal role in automated test frameworks such as what is Selenium webdriver, allowing QA Engineers to efficiently find and interact with elements. By mastering advanced XPath methods, you can fix challenges like nested structures, dynamic IDs, and asynchronous updates, guaranteeing your testing remains steady and accurate.
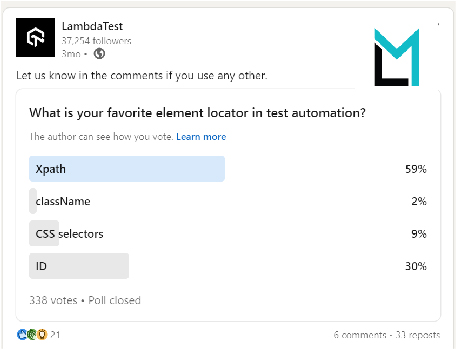
According to a recent LambdaTest poll, 59% of participants chose XPath over alternative element locator, making it the most popular locator for test automation.
In modern automated testing frameworks like Selenium, mastering XPath offers unparalleled precision and flexibility when interacting with web components, particularly in complicated and robust environments. Now find out why mastering XPath is crucial in Test Automation:
1. Particular Element Location
It allows QA Engineers to pinpoint elements within a page based on hierarchical relationships, multiple attributes, and text content. This is chiefly beneficial when:
- Other locators fail: When name, ID, or class locators are inaccessible or unreliable, XPath provides a robust alternative.
- Dynamic elements exist: It enables you to locate elements through relative positioning or partial matches, making it suitable for frequently changing or dynamic web elements.
2. Scalability in Locator Strategies
XPath supports both relative and absolute paths:
- Relative XPath: Use relationship to find elements (e.g., //div[@class=’header’]).
- Absolute XPath: Traverses the complete Document Object Model (DOM) hierarchy (for instance, /html/body/div[1]).
The flexibility to utilize relative paths guarantees that your scripts are resilient to alterations in the Document Object Model (DOM) structure.
3. Navigating Complicated and Nested Structures
Web apps often embrace intricately structured or deeply nested elements. XPath offers robust features to navigate such structures using:
- Text Matching: Find elements based on partial or exact text matches (text(), contains()).
- Axes: Navigate between parent, child, sibling, and ancestor relationships (parent::, child::, following-sibling::).
For example, accessing a deeply nested button may seem like this:
//div[@class=’container’]/child::div[@class=’content’]/button.
4. Managing Dynamic Attributes & IDs
Robust pages often create classes and IDs that change with every session or user communication. XPath’s capacity to utilize:
- Stable Parent Elements: Locate components based on a parent with a constant attribute.
This guarantees that scripts can accept changes without breaking. - Partial Matches: Match portions of an attribute (for instance, contains() or starts-with()).
5. Better Debugging with XPath Testers
XPath testers (such as browser DevTools or standalone tools) enable QA Engineers to authenticate XPath expressions before using them in test scripts. This assists:
- In rapidly check XPath accuracy.
- In optimizing expressions for consistency and performance.
Mastering XPath comprises leveraging these tools for test script development & effectual debugging.
6. Cross-Browser and Framework Incorporation
Several test automation tools like TestNG, Selenium, and Appium, depend extremely on XPath for detecting web elements. By mastering XPath, QA Engineers can:
- Improve the consistency of scripts in any automated test framework.
- Create reusable locators across several platforms & browsers.
7. Confirming Test Resilience
XPath’s versatility guarantees that testing is extremely resilient to changes in the app’s User Interface. When used efficiently, it:
- Lessens flakiness in tests.
- Improves scalability and manageability of test scripts.
Mastering XPath isn’t simply a technical skill but a cornerstone of effectual automated tests. It empowers QA Engineers to build acceptable, powerful, and maintainable test scripts that excel in managing complicated, dynamic web apps.
Explore Further: Keala Scherzinger: The Realtor Sister of Pop Star Nicole Scherzinger
How can Cloud-powered platforms like LambdaTest assist with XPath Tests?
LambdaTest is a robust cloud-based test platform that eases and improves XPath tests in multiple modes. Here’s how it can assist:
- Cross-Browser Tests at Scale
LambdaTest enables you to implement XPath-centric scripts across 1000s of OS and browser combinations. This confirms your XPath expressions work constantly across several environments, including earlier browser versions, which can have changing DOM structures.
- Smooth Selenium Integration
The platform is fully compatible with Selenium, allowing you to run test scripts that leverage XPath locators directly on its cloud-based infrastructure. This eliminates the need for local browser setups and enhances the scalability of your test execution. Integrating automated visual testing here helps validate not only element presence but also visual alignment, layout stability, and pixel-perfect rendering across browsers.
- Real-Time XPath Validation
With LambdaTest’s live tests feature, you can authenticate & debug your XPath expressions in real time. Just scrutinize elements within the live browser & ensure XPath queries find the desired items by testing them in real-time.
- Managing Dynamic Elements & IDs
By executing XPath-based testing in parallel on various gadgets, web browsers, and devices, LambdaTest significantly decreases test implementation time. This is chiefly beneficial for large-scale regression testing, where XPath locators are extensively used.
- Parallel Tests for Effectiveness
By executing XPath-based testing in parallel on various gadgets and web browsers and devices, LambdaTest significantly decreases test implementation time. This is chiefly beneficial for large-scale regression testing where XPath locators are extensively used.
- Debugging with Modern Developer Tools
The platform also includes advanced developer tools, allowing you to inspect the DOM structure of pages in detail. Such tools can easily be utilized to create and test XPath expressions effectively.
- Device and Geolocation Tests
Test your XPath locators on PCs and mobile with diverse geolocations, guaranteeing compatibility across multiple user environments. This is vital for global apps with different user bases.
- Test Insights & Analytics
LambdaTest provides comprehensive reports and analytics, assisting you in detecting and fixing issues with XPath expressions or automated test scripts. Insights into failures caused by synchronization problems or incorrect locators can considerably enhance test reliability.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, mastering XPath is crucial for generating adaptable and robust automated test scripts. XPath’s capacity to manage complicated DOM hierarchies, nested structures, and dynamic attributes, makes it a robust tool for navigating and interacting with advanced, dynamic web apps. To further improve the reliability and effectiveness of your test efforts, incorporating cloud-powered platforms such as LambdaTest can be a game-changer. With this incredible platform, you can confidently authorize your XPath expressions and perform automated testing across multiple platforms, guaranteeing optimal test accuracy and coverage.