Simon Luckinbill is the oldest son of Lucie Arnaz and Laurence Luckinbill, born into a family of Hollywood legends. He is also the grandson of Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz, names that shaped American television. Unlike many celebrity children, Simon built his own path as a visual artist, keeping a private life but sharing his creativity through colorful paintings. His story is one of heritage, talent, and quiet strength.
Quick Bio Table
| Fact | Details |
| Full Name | Simon Thomas Luckinbill |
| Birth Date | December 10, 1980 |
| Age | 44 (as of 2024) |
| Parents | Lucie Arnaz & Laurence Luckinbill |
| Grandparents | Lucille Ball & Desi Arnaz |
| Nationality | American |
| Siblings | Joseph Luckinbill, Katharine Luckinbill, 2 half-brothers |
| Profession | Visual Artist (Painter) |
| Known For | Paintings, Art Shows in Palm Springs |
| Education | Focus on art and visual studies |
| Notable Exhibits | Archangel Gallery, Gallery 500 |
| Net Worth | Estimated $1M–$2M (unverified) |
| Lifestyle | Private, family-centered, art-focused |
Early Life and Family Heritage
Simon Luckinbill was born on December 10, 1980, in Los Angeles, California. His family background placed him in the center of American entertainment history. His mother, Lucie Arnaz, is an accomplished actress and singer, while his father, Laurence Luckinbill, is an actor and playwright. Simon is also the grandson of Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz, television icons whose influence remains strong decades later.
Growing up, Simon was surrounded by creativity. His childhood was filled with the energy of a family that lived and breathed performance and art. While he inherited the legacy of acting and show business, Simon decided to find his own path. Instead of stepping into film or television, he focused on painting and visual arts.
Childhood and Siblings
Simon spent his early years in California with his siblings Joseph and Katharine, along with two half-brothers from his father’s earlier marriage. Family life mixed the glamour of Hollywood with ordinary routines. Even though his parents were in the spotlight, they worked to provide a stable and supportive home.
Discover More: Natalie Oglesby Skalla: An In-Depth Look at Her Life, Career, and Impact
Unlike his mother and grandparents, Simon avoided public fame during his youth. He grew up quietly, focusing on personal interests rather than the pressure of acting. The decision to pursue painting allowed him to express himself without the constant attention that often follows celebrity families.
Education and Early Interests
Although exact details of his schooling remain private, Simon showed a strong interest in art from a young age. He explored painting techniques and studied visual storytelling. His choice to invest in creativity showed early signs of a unique path.
Friends and family recall that Simon had a natural eye for color and shape. His passion for painting allowed him to blend emotion with style, making his works both personal and powerful. This foundation later grew into a professional art career.
Career Path as a Visual Artist
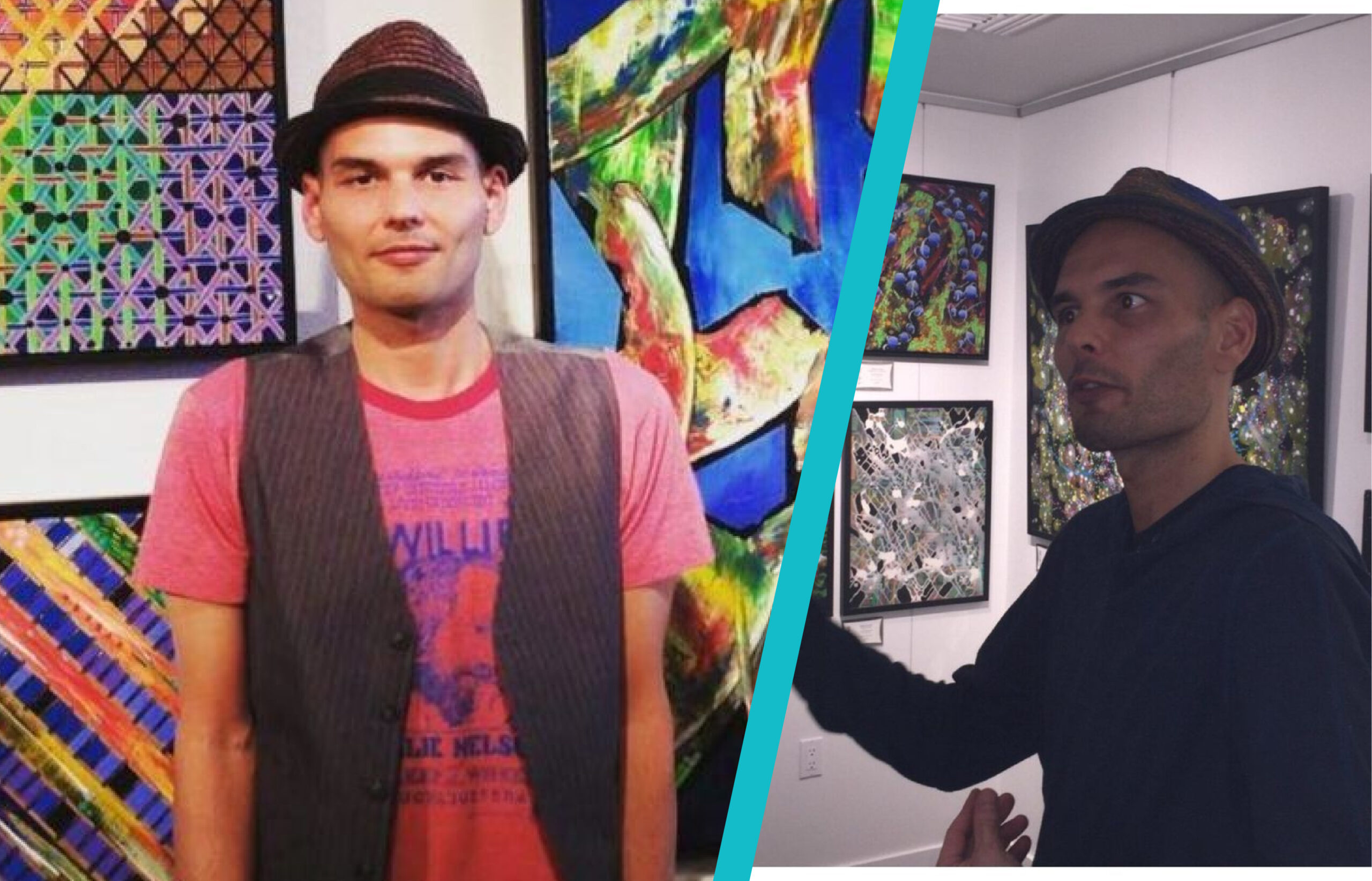
Simon Luckinbill became a professional artist, choosing painting as his main form of work. He creates vibrant acrylic paintings that often reflect music, emotion, and faith. His bold style is recognized for layering, texture, and striking colors.
He is not an actor or public speaker like his parents, but his art has brought him recognition in galleries. Simon explained in interviews that art is his way to share feelings and ideas, without needing the spotlight of Hollywood.
Major Exhibitions and Achievements
Simon’s art career became public through exhibitions in Palm Springs. He first gained attention at the Archangel Gallery, where his work impressed visitors. Later, he presented paintings at Gallery 500, which drew collectors and art lovers.
Reports said that one of his openings had extraordinary success, with more than half of his paintings sold within a short time. For Simon, this moment was proof that his work connected with people beyond his famous family name. His career shows he is valued as an artist in his own right.
Artistic Style and Themes
Simon’s paintings often use acrylic on canvas. His art blends emotional storytelling with visual detail, exploring themes like love, spirituality, and human connection. Bright colors and layered textures are his trademarks.
He once described painting as a way to “paint feelings” rather than objects. This personal approach allows him to communicate deep meaning without words. Collectors often describe his works as both inspiring and comforting.
Relationship with Famous Family
Being the son of Lucie Arnaz and Laurence Luckinbill means Simon’s name always connects back to Hollywood. His grandparents, Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz, are legends whose shows still air around the world. This family link makes people curious about Simon’s life.
Despite this legacy, Simon avoids the entertainment industry. Instead, he shares his creativity through painting. This independence shows his desire to build his own identity, while still honoring the influence of his family.
Net Worth and Earnings
Like many private figures, Simon Luckinbill does not publish financial records. However, estimates suggest his net worth is between $1M and $2M. These numbers come from his art sales, exhibitions, and commissions.
Compared to his mother and grandparents, Simon’s wealth is smaller, but his achievements reflect dedication rather than fame. Each exhibition and sale adds to his recognition and builds his legacy as a painter.
Personal Life and Privacy
Simon prefers a quiet life. Unlike many celebrity children, he does not use fame for attention. His presence on social media is limited, and most public photos come from posts by Lucie Arnaz, who often shares birthday tributes or family celebrations.
This privacy allows Simon to focus on what matters: his art and his family. Fans respect his decision to live away from constant media pressure while still continuing creative work.
Relationship with Mother Lucie Arnaz
Simon’s bond with his mother is strong. Lucie Arnaz has often spoken proudly about her children, calling motherhood one of her greatest joys. She shares warm messages about Simon on Instagram, celebrating his birthday and artistic success.
Through her posts, fans see glimpses of Simon’s life and personality. The love and support between mother and son highlight the importance of family in his journey.
The Luckinbill Legacy
Simon carries forward a remarkable family legacy. With grandparents like Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz, his family name is tied to television history. His father and mother also built careers on stage and screen.
Even so, Simon stands out by choosing art instead of acting. This choice adds variety to the family legacy, showing that creativity can take many forms. His story proves that success does not always follow the same path.
Lessons from Simon’s Journey
The story of Simon Luckinbill teaches that fame is not the only road to success. He shows that dedication to passion, even outside the spotlight, can create meaning. His decision to focus on painting proves that identity can be built on personal values rather than public expectation.
Further: Maura Ddhu Studi Net Worth: How Rich Is Wes Studi’s Wife?
Simon is an example for those who want to live privately but still share their talents. His life inspires people to respect their heritage while creating their own way.
Conclusion
Simon Luckinbill is the son of Lucie Arnaz and Laurence Luckinbill, and the grandson of legendary entertainers Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz. Born in 1980, Simon grew into a professional visual artist known for bold acrylic paintings. His exhibitions in Palm Springs gained attention and success.
While his net worth is modest compared to celebrity relatives, Simon’s life shows balance, creativity, and independence. His story is proof that family legacy is powerful, but true fulfillment comes from following one’s own passion.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Who is Simon Luckinbill?
He is the son of Lucie Arnaz and Laurence Luckinbill, and the grandson of Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz.
2. What does Simon Luckinbill do for a living?
He is a professional visual artist and painter.
3. Where has Simon Luckinbill exhibited his art?
He has shown work at Palm Springs galleries, including Archangel Gallery and Gallery 500.
4. What is Simon Luckinbill’s net worth?
It is estimated between $1M and $2M, though exact figures are unverified.
5. Is Simon Luckinbill active in Hollywood?
No, he chose to work in art instead of acting or film, unlike his parents and grandparents.